Supplement Spotlight #7: Berberine
An overview on a natural metabolic optimization tool. 13 brands ranked by potency.
Let’s clarify something up front: berberine is not “Nature’s Ozempic” (*cringe*).
The headlines overplayed its efficacy the past few years. But, it’s still what I’d consider one of the most powerful compounds in the metabolic health space. I’ve personally seen a robust set of benefits for lipid markers especially (triglycerides & LDL-C reduction) & improvement of short-term glycemic response during a series of continuous glucose monitor tests in 2023. As we’ll see, there’s been a compelling body of research in the past 2-3 years supporting berberine’s utility as a metabolic optimization tool.
What we’ll cover:
What is Berberine?
How it Works
Benefits (as seen through the latest research)
Protocol
13 Brands Ranked (by lab tested data)
What is Berberine?
Berberine use dates back 3,000 years ago to 650 BC where evidence of the barberry fruit (Berberis vulgaris) being used as a blood purifying agent was discovered on the clay tablets in Assyrian emperor Asurbanipal’s library.

In Ayurvedic medicine, variations of berberine traditionally addressed a wide spectrum of conditions including ear & mouth infections, wound healing, scorpion & snake bites, digestive disorders, & even obesity (yes - fat people existed centuries ago too!)
Similarly in traditional Chinese medicine, berberine derivatives were used as a tool to eliminate toxins, “purge fire”, & “clear heat in the liver”.
Chemically, berberine is classified as an isoquinoline alkaloid with the molecular formula C₂₀H₁₈NO₄.
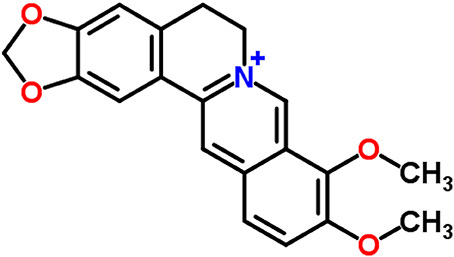
Mechanisms of Action
Activation of AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK)
Berberine activates a key enzyme (AMPK) - typically known as our body's “metabolic master switch”. Berberine helps to flip this switch by slightly lowering our cells' ATP (energy) signaling to our body it needs to make better use of its fuel.
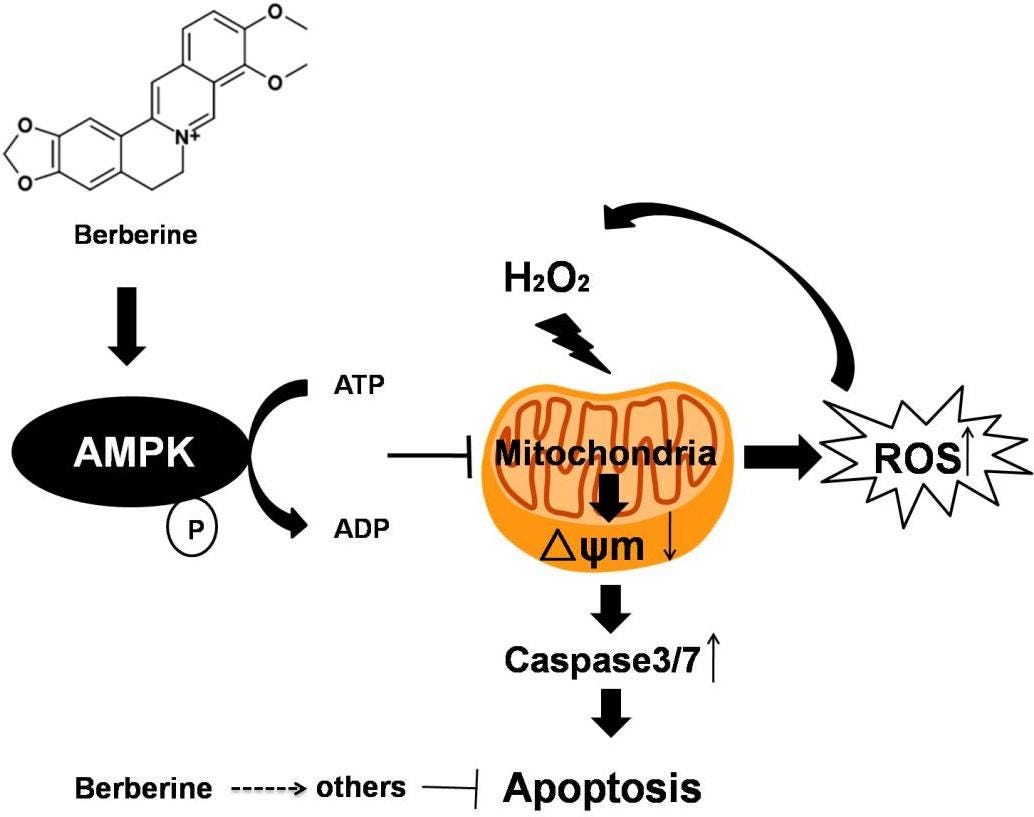
As a result:
Our cells pull more glucose from the bloodstream helping lower blood sugar levels.
Fat gets broken down more easily & used for energy.
Fat & glucose production in the liver slows down.
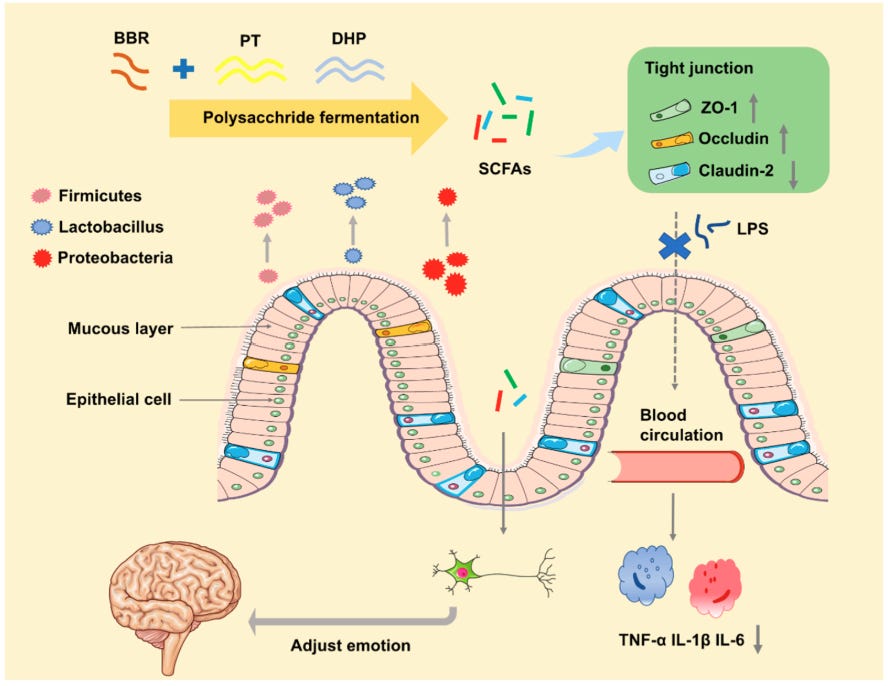
Modulation of Gut Microbiota
An underrated benefit we’ll touch on is berberine’s ability to rebalance our gut microbiome. It functions by increasing the “good” bacteria like Akkermansia muciniphila & others that produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) → compounds fortifying our gut barrier. It also reduces harmful bacteria like E. coli & Enterococci, both known to damage the gut barrier and lead to inflammation inside the gut.
Inhibition of α-Glucosidase
Another way berberine helps control blood sugar is via blocking an enzyme in our gut called α-glucosidase. Its job is to break down complex carbs into glucose so that your body absorbs it efficiently.
By slowing down this process, berberine reduces the rate at which sugar enters our bloodstream after a meal → prevents sharp blood sugar spikes. (more on that later)
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Berberine suppresses inflammation by targeting a major component in our body’s inflammatory response: a protein complex called NF-κB.
NF-κB acts like an emergency alarm switching on genes responsible for producing pro-inflammatory molecules. Berberine reduces the production of inflammatory compounds like TNF-α, IL-6, & COX-2.
By lowering these markers, berberine decreases systemic inflammation → helpful for the management of CVD, insulin resistance, & metabolic syndrome.
Health Benefits
The recurring theme you'll see across many of the benefits presented here: metabolic health optimization. Like any supplement discussed, I'll reemphasize a couple key principles to guide your supplementation protocol:
Cycle these compounds over time.
Remember that nearly any intervention can be deemed impactful - as long as the subjects are unhealthy enough.
Metabolic Health
Type 2 Diabetes
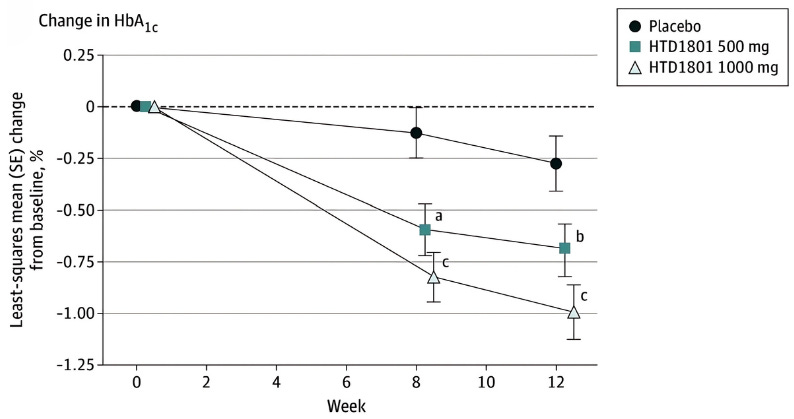
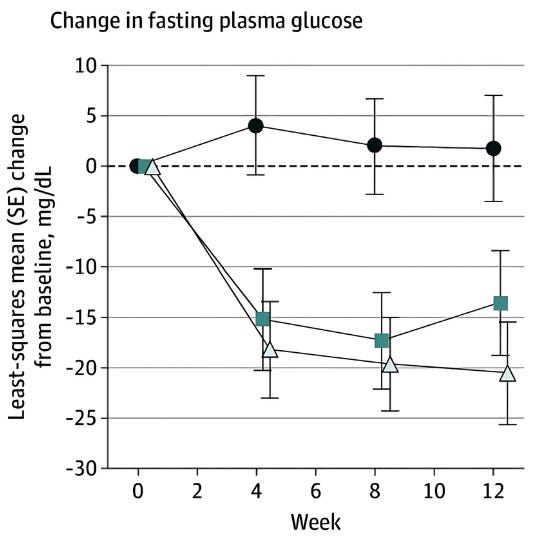
One of the most robust trials for berberine's metabolic case was published recently in March 2025. For a 12-week period, 113 adults with type 2 diabetes were assigned to a placebo, 500 mg (2x daily), or 1,000 mg (2x daily) group.
Those receiving 1,000 mg 2x daily achieved clinically significant HbA1c reductions (-0.7% vs. placebo) with 55% reaching target HbA1c <7% & 30% below 6.5%.
The 1,000 mg berberine group also significantly improved fasting blood glucose (-18.4 mg/dL).
Glycemic Control
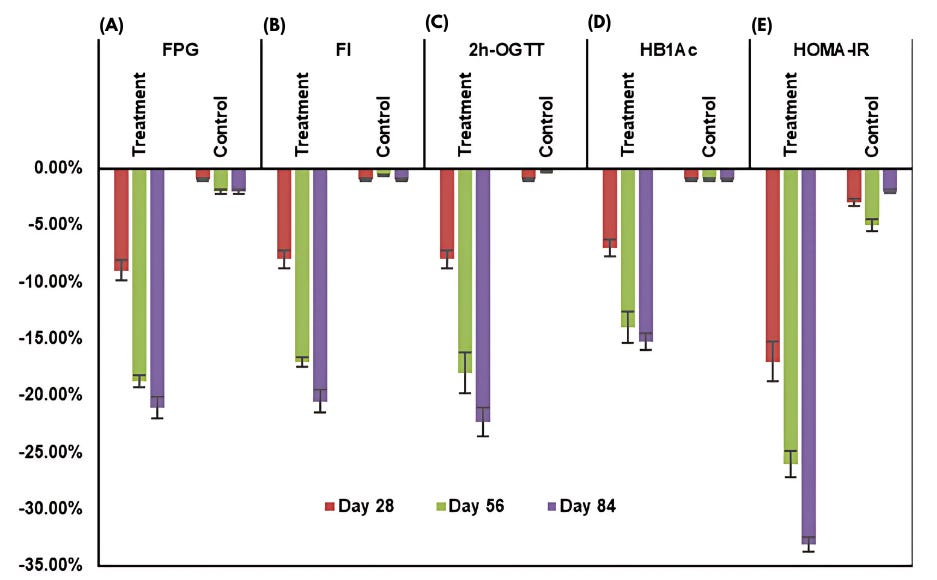
A 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial investigated berberine's effects on glycemic control in 34 prediabetic individuals. Those receiving berberine 3x daily at 500 mg/dose showed significant reductions relative to the placebo group across multiple metabolic biomarkers:
Reduced fasting blood glucose by 21% (from 6.75 to 5.33 mmol/L)
Reduced fasting insulin by 20% (from 9.81 to 7.88 µIU/mL)
Reduced 2-hr oral glucose tolerance by 22% (from 10.44 to 8.12 mmol/L)
Reduced HbA1c by 15% (from 6.40 to 5.43%)
Improved insulin sensitivity by 33% (from 3.61 to 2.41)
Another 20-week randomized controlled trial evaluated berberine’s efficacy in managing metabolic syndrome among people with HIV on antiretroviral therapy. Subjects with the virus were split into placebo & treatment (500 mg 3x daily) groups. Following the 20-week period, the berberine group showed significant improvements in metabolic parameters compared to placebo across the following metabolic biomarkers:
Reduced triglycerides by 34% (from 180 to 118 mg/dL)
Reduced TNF-α by 43% (from 2.3 to 1.3)
Reduced BMI by 1.2% (from 83 to 82 kg)
Lipids
A meta-analysis across 41 RCTs & nearly 5,000 subjects evaluating berberine's lipid-lowering effects comparing its efficacy as a standalone therapy and in combination with other nutraceuticals.
On average, berberine alone significantly reduced triglycerides by -17.40 mg/dL & LDL-C by -9.26 mg/dL.
Another meta-analysis focused on lipid-specific biomarkers evaluated berberine’s lipid-modifying effects in 18 randomized controlled trials & nearly 1,800 subjects. Some of the findings included:
Reduced LDL-C by 23.2 mg/dL
Reduced triglycerides by 30.1 mg/dL
Reduced ApoB by -0.25 g/L
In a 60-day, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Berberine Phytosome was administered at 550 mg 2x daily in 49 overweight individuals with dysfunctional glucose metabolisms. After 60 days, the berberine group showed significant metabolic improvements compared to placebo:
Reduced fasting glucose by 6.7 mg/dL
Lowered triglycerides by 12.4 mg/dL
Reduced visceral fat levels by 91.5 g
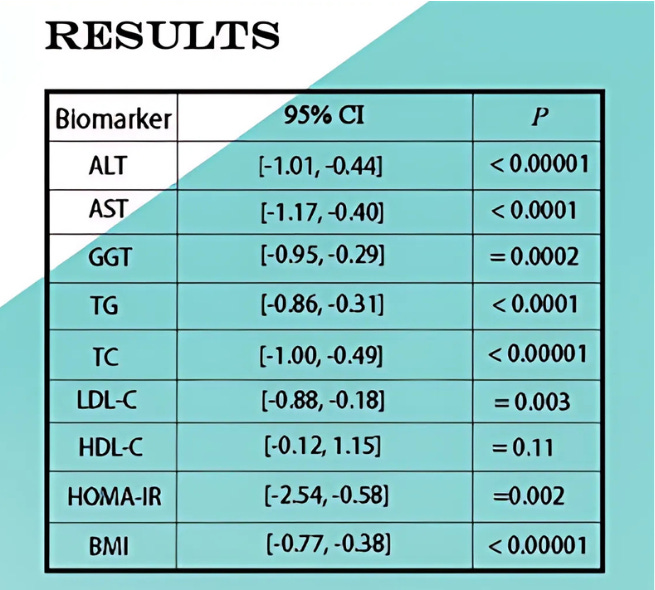
NAFLD
A meta-analysis of 10 randomized controlled trials across more than 800 patients demonstrated berberine’s efficacy in improving metabolic & hepatic biomarkers associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD):
Gut Health
One use case we'll see more of in the next decade is berberine's utility as a tool for improving the state of the gut microbiota.
Gut Microbiome & Inflammation
This randomized controlled trial investigated berberine hydrochloride’s effects on gut microbiota & inflammation in 68 Parkinson’s disease patients. Berberine supplementation showed several significant improvements across biomarkers:
Reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines: IL-8, IL-6, and TNF-α levels decreased significantly in the berberine group compared to controls
Increased microbial diversity: Higher Chao index, Ace index, and Shannon index in the berberine group, indicating restored microbial richness and diversity
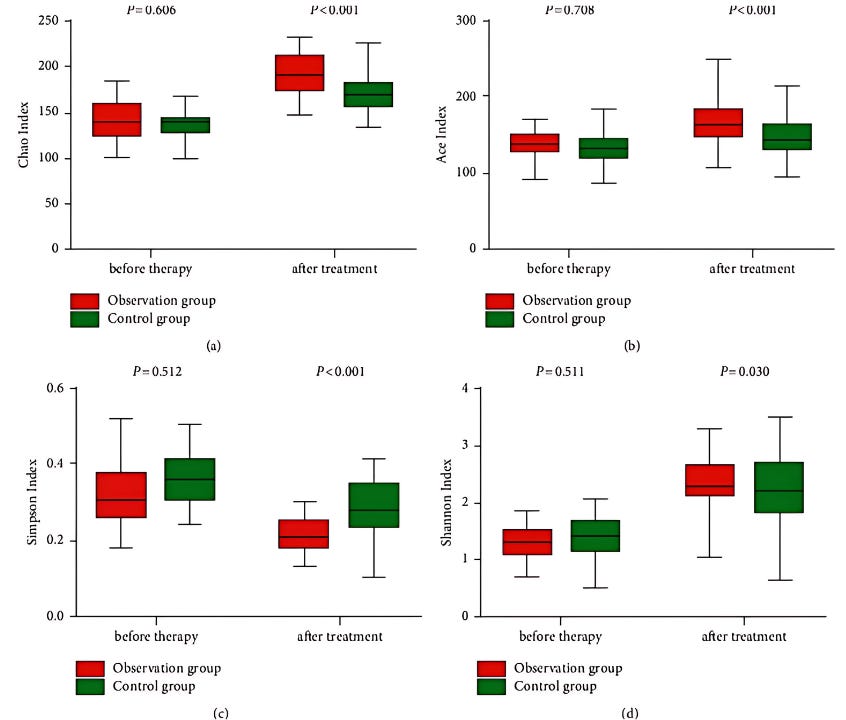
Lower Simpson index (reduced dominance of single species) → suggests a more balanced microbiome
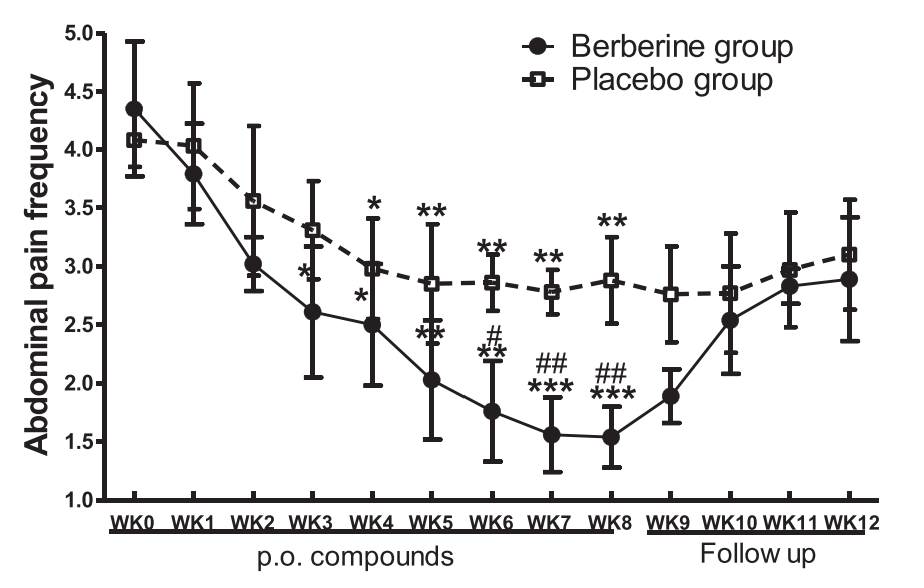
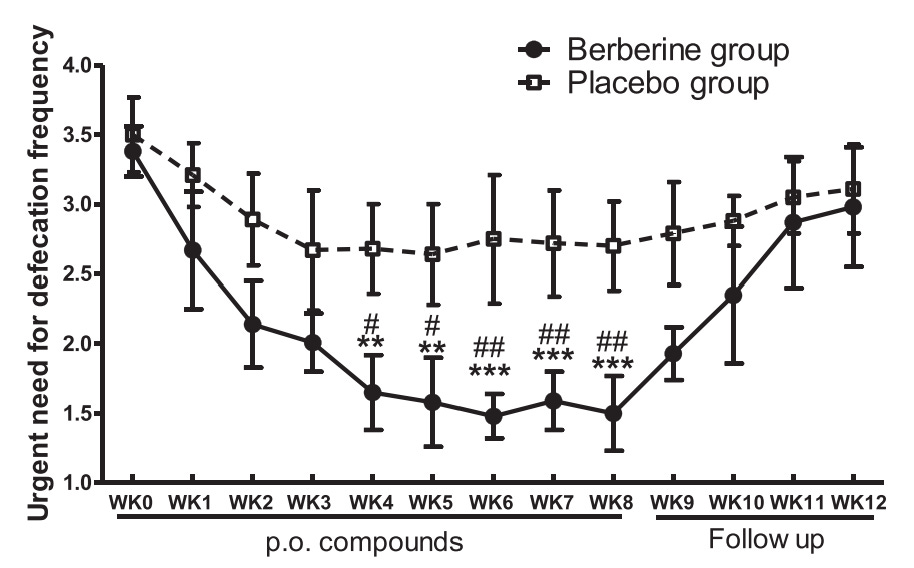
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 196 patients with IBS, the berberine group (400 mg /day) saw significant improvements across multiple symptoms relative to the placebo group:
Reduced abdominal pain
Reduced urgent bowel movements
Improved overall quality of life scores
Decreased depression & anxiety metrics
Decreased diarrhea frequency
Chronic Inflammation
In a meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials & 1,600 participants, berberine supplementation significantly reduced inflammatory biomarkers: interleukin-6 (IL-6) by -1.18 pg/mL, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) by -3.72 pg/mL, & C-reactive protein (CRP) by -1.33 mg/L relative to the control groups.
PCOS
Given berberine’s ability to improve conditions of insulin resistance, it’s also become a robust tool for improving polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) symptoms.
This meta-analysis included 713 participants across 10 randomized controlled trials. Compared to Western medicine treatment alone, results showed berberine combined with Western medicine significantly improved endometrial thickness (1.62 mm increase), ovulation rate (41% higher), & clinical pregnancy rates (96% higher).
Protocol
The following protocol was developed based on a combination of user feedback, personal research, & clinical *human* trials. Subjects are assumed to be 180 lb males with a dialed-in health foundation (i.e. sleep + movement + light environment + resistance training + nutrition).
Dosage: 500 mg (2-3x daily)
Timing: Ideally taken before meals (especially high carbohydrate meals) to reduce post-prandial glycemic spikes
Duration: 12-16 weeks - ideally test metabolic & hepatic biomarkers prior to administering and immediately following the cycle period
Reputable Sources
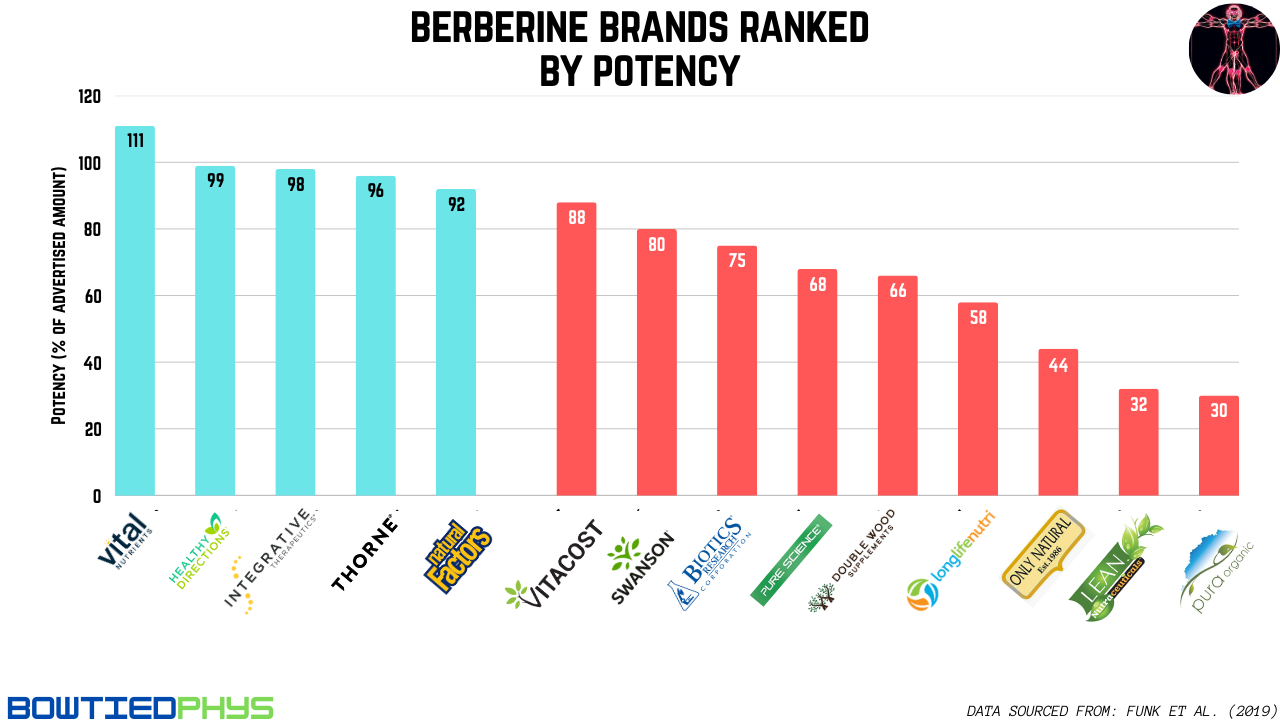
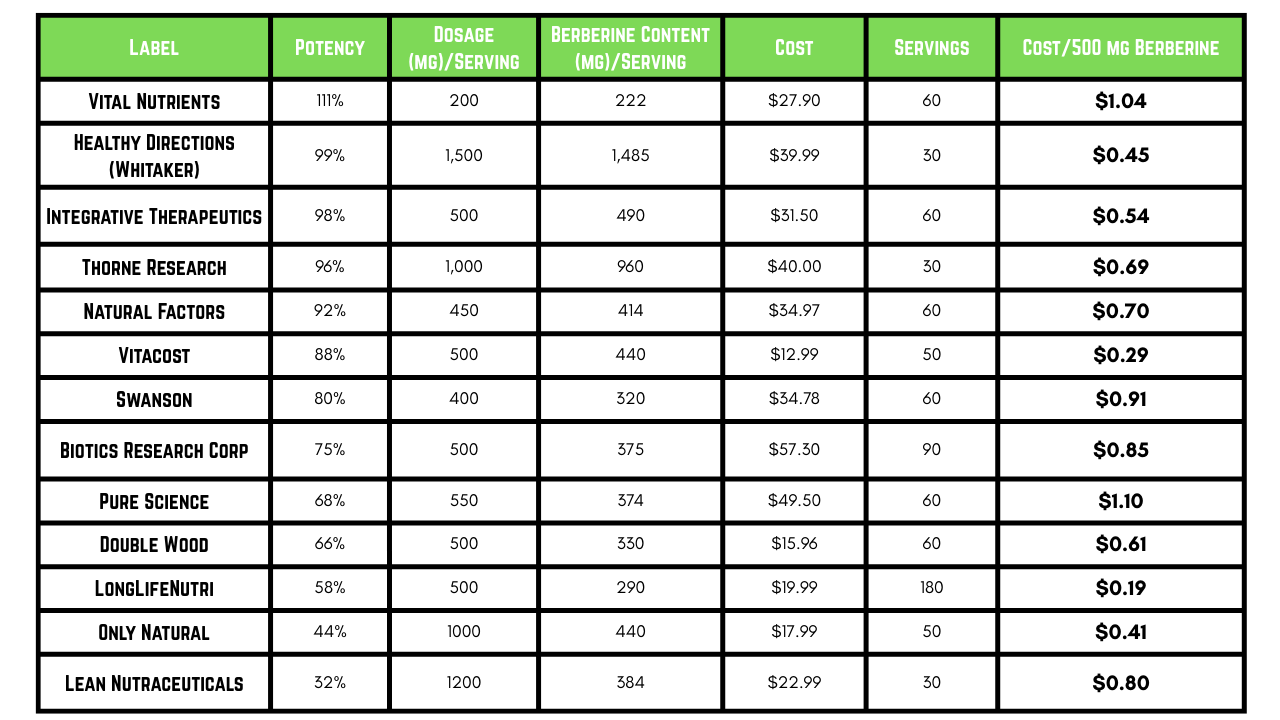
In 2019, a group of biochemists & pharmacists conducted potency testing on 15 berberine supplements & reported the results in this paper.
I cleaned the data up providing a plot below of these products:
Now using the current cost (as of April 12, 2025), all berberine products are listed below with a standardized cost ($)/500 mg berberine content:
Based on the combination of these data, Consumer Lab reports, & user feedback, the brands I trust are those represented with the potencies measuring > 90% (or if not measured have consistently trustworthy reputations):
**Dr. Whitaker Clinical Grade Berberine (Healthy Directions)** (Phys Value Pick)
Cost/500 mg: $0.45
*Vital Nutrients Berberine*(Phys Overall Quality Pick)
Cost/500 mg: $1.04
Cost/500 mg: $0.69
Integrative Therapeutics Berberine
Cost/500 mg: $0.54
Pure Encapsulations Berberine UltraSorb
Cost/500 mg: $0.75
We’re more bullish than ever on the future here. As always, stay healthy & we’ll see you next week.
Your friend,
BTP
***Disclaimer: The information provided by BowTiedPhys is for educational purposes only. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment of any kind. BowTiedPhys is not a licensed medical provider. Prior to making any changes to your health protocols, consult a licensed healthcare professional. Some of the links in this post may be affiliate links - BowTiedPhys may earn a commission at no additional cost to you. This commission helps support our work and allows us to continue providing valuable content to our valued subscription members.***











Great article. Would it be best to skip berberine with a pre lifting meal and post lift meal?